While installing VMware vCenter 5.0 on a Windows Server 2008 R2 isn’t very exciting, I had to document one of my installs earlier last week so while it doesn’t differ too much from 4.x, I thought I’d take the screenshots I took and write a blog post in case anyone wants to see what it looks like.
Download and double click on the autorun file:

Once the VMware vCenter Installer launches, proceed with selecting vCenter Server and click on install:
Note that I ran this install on a Windows Server 2008 R2 64-bit w/SP1 server and it was not necessary for me to manually install the Prerequisites:
1. Microsoft .NET 3.5 SP1
2. Windows Installer 4.5

The installer for vCenter 5.0 will now launch:


Agree to the EULA:
Type in the appropriate values for the fields:

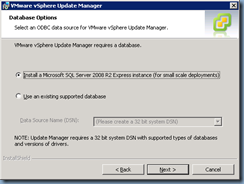
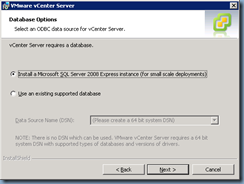
As with vCenter 4.x, you’ll have the option of using a local SQL install or a full blown remote SQL server:
You can choose to use a local or domain service account or the SYSTEM Account to run the service:

Note that if you don’t have a DNS entry for your host or if the server is unable to contact a DNS to verify that a record has been created for its name, you’ll receive the following warning:
The Fully Qualified Domain Name cannot be resolved. If you continue the installation, some features might not work correctly. For detailed requirements, see the vSphere Installation Setup guide.

Proceed with the install:








Notice that if you chose to use a local SQL instance as your database, the installer will launch the SQL Server 2008 R2 installer:




Once the installation of the local instance of SQL completes, the installer will proceed with the vCenter components:








… and we’re done.